To do this place a drop of water towards one end of the slide. While observing the leaf under the microscope wick a solution of 6 NaCl sodium chloride across the slide.
This movement of water may be harmful to cells.
Plasmolysis in elodea cells. Observe the cells under normal conditions and make a sketch of what you see. While observing the leaf under the microscope wick a solution of 6 NaCl sodium chloride across the slide. With the same leaf try wicking distilled water across the slide.
PLASMOLYSIS IN ELODEA CELLS. PLASMOLYSIS IN ELODEA CELLS Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration. This movement of water may be harmful to cells.
A hypertonic solution can result in the plasmolysis of a cell when the water in a. To do this place a drop of water towards one end of the slide. Using forceps remove a small leaf from the tip of an Elodea plant and lay it flat in the drop of water.
Cover with a cover slip. Observe the leaf at 40X and record your observations. Increase the magnification to 100X observe and record your observations.
When plant cells are placed in a hypertonic solution they undergo plasmolysis in which much of the water exits the cell and the plasma membrane pulls inwardthe cell wall however retains its shape. When a plant cell has sufficient water in its cytoplasm the cell maintains is shape by exerting turgor pressure onto the cell wall. As water flows in and the solutes cannot flow out the increased numbers of molecules inside the cell.
Watch as Elodea cells lose water when placed in a strong salt solution. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube. Observing Elodea Leaves and Plasmolysis In this lab we observed elodea leaves with different solutions on them using microscopes that produced magnifications of 100 times and 400 times.
We observed elodea leaves with drops of water on them we dropped a ten percent solution of salt and water on the elodea leaves and we later observed the elodea leaves with distilled water on them after the. The cell membrane has pulled away from the cell wall marking the onset of plasmolysis called incipient plasmolysis. Elodea can be found in wet mud along sluggish streams seepage areas and marshes.
Pros and Cons of Elodea Elodea has no known direct food value to wildlife. Plasts were the plasmolysis of the cells and enzymatic removal ofthe cell wall we examined the effects of plasmolysis onthe electrical parameters ofleafcells. Elodea leaves proved mostamenablefor this study.
After adding 07M mannitol to the bathing medium surrounding the leaves weobservedthat the large nega-tive membranepotential waschanged to a positive voltage following plasmolysis of. Virginiana cells in CLSM and FESEM. A Round protoplasts after plasmolysis in 05 M sucrose and stained with DioC 6 3 show Hechtian strands arrows connecting the plasmolysed.
Also to know when an elodea leaf is placed in a concentrated salt solution. Plasmolysis is the shrinking of the cytoplasm of a plant cell in response to diffusion of water out of the cell and into a high salt concentration solution. Plasmolysis in Elodea Plant Cells Name _____ Methods Elodea in Tap Water 1.
Prepare a wet mount of an Elodea leaf with tap water. To do this place a drop of water towards one end of the slide. Using forceps remove a small leaf from the tip of an Elodea plant and lay it flat in the drop of water.
Cover with a cover slip. Observe the leaf at 40X and record your observations. Create a hypothesis for the experiment described below.
Obtain a leaf of Elodea and place it on a blank microscope slide. Dry it with a paper add a drop or two of 10 NaCl and then cover it with a cover slip. Observe the cells under scanning and.
4 Observe plasmolysis in Elodea. Background Osmosis is the process whereby water moves across a cell membrane by diffusion. Diffusion takes place when the molecules of a substance tend to move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration.
The process of osmosis must be tightly controlled by cells otherwise they will die. For example if you place a red blood. Plasmolysis only occurs in extreme conditions and rarely occurs in nature.
It is induced in the laboratory by immersing cells in strong saline or sugar sucrose solutions to cause exosmosis often using Elodea plants or onion epidermal cells which have colored cell sap so that the process is clearly visible. A likely structural evolution of the cytoplasm of cells undergoing plasmolysis could be a possible cause of this instability 8. On the other hand corresponding observations in the vacuole show relatively stable potentials for higher levels of saccharose.
A have therefore adopted for our measurements a delay of about Z5 min after the introduction of the microelectrode with three of four. Plasmolysis In Elodea Leaf Cells Victoria Newton Chloroplasts In The Leaf Cells Of Elodea Canadensis Canadian Waterweed 2008 Photomicrography Competition Nikon S Small World Botany Lab Practical Flashcards Quizlet. This is because water will be drawn out of the vacuole through osmosis the protoplast will shrink and the plasma membrane will actually pull away from the cell wall plasmolysis resulting in a loss of turgor pressure.
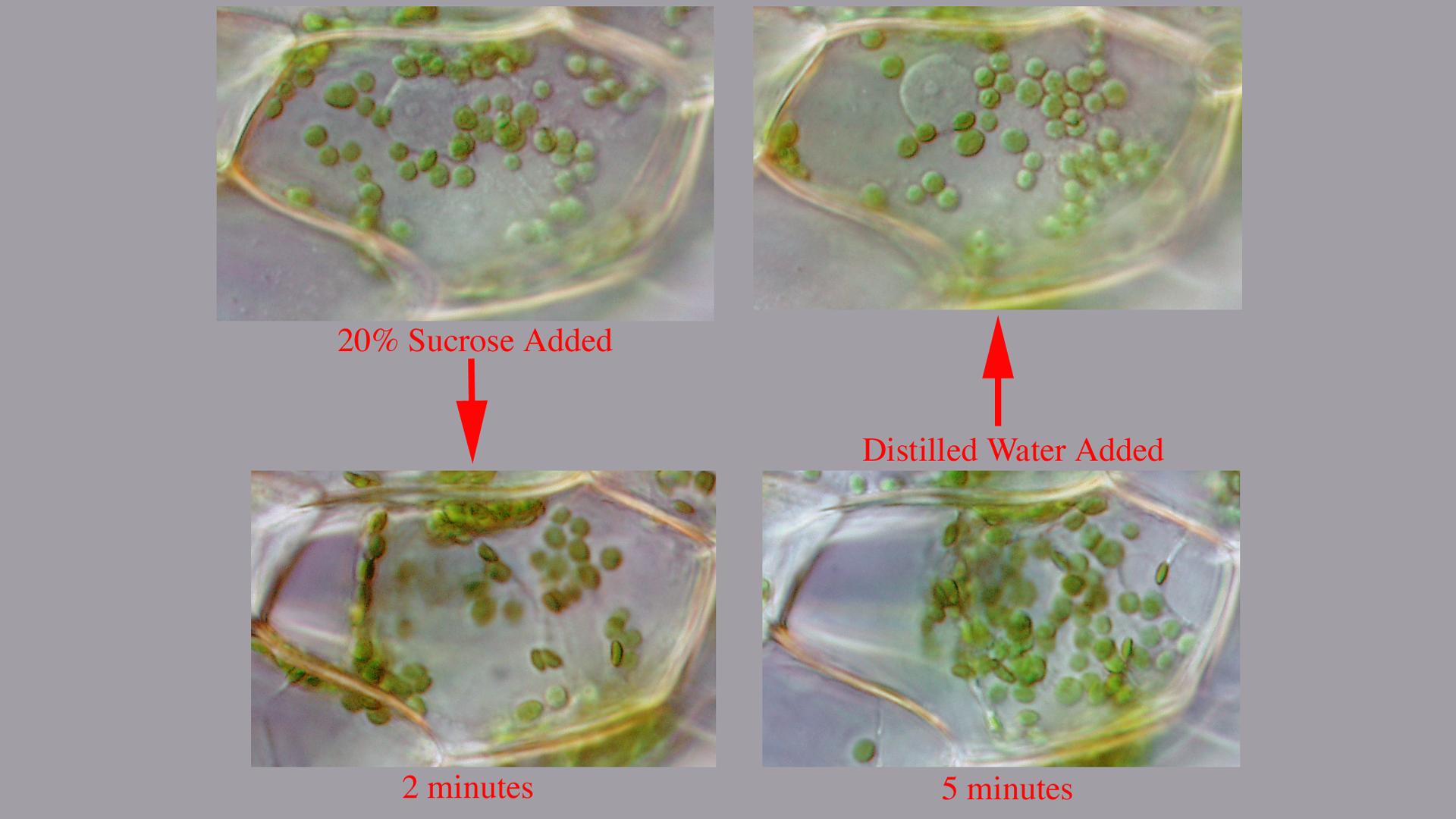
The following image shows an Elodea leaf that was placed in a 20 sucrose sugar solution. Note how the inside of the cell is shrinking and the gap between the plasma membrane and the cell wall the cell.
